| |
Introduction to Chain Codes
ABSOLUTE
CHAIN CODES
 DIRECTIONAL
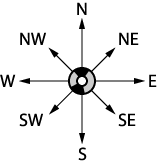
SYSTEM: Points of a compass DIRECTIONAL
SYSTEM: Points of a compass
The points of the compass give us an absolute
set of reference points, it is fixed by the Earth's magnetic fields.
We can also fix the direction points to something smaller (like a piece
of paper for example, or the computer monitor). The top = N, bottom
= S, etc.
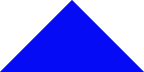
The chain code that we just produced is an algorithm
that gives a symbolic representation of the triangle's shape, size and
orientation. This information also provides precise rules for reconstructing
that figure in a drawing. We will typically write the chaincode in one
of either two ways. Either as
After you've written down the complete chain code,
click the button that says "Completed Chain Code" below, and
see if you got it right.
Using numbers in writing chain codes
 Since digital computers typically use a numerical system for
storing information (everything is coded in "O's" and "1's")
it will be a step in the right direction to modify our directional system
to a numerical system rather than a letter system. Computer programmers
typically use this system.
Since digital computers typically use a numerical system for
storing information (everything is coded in "O's" and "1's")
it will be a step in the right direction to modify our directional system
to a numerical system rather than a letter system. Computer programmers
typically use this system.
INSTEAD OF
Relative
chain codes
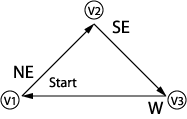
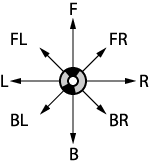 It
is possible to base an eight-directional coding system on relative directions.
Each of the eight directions will be defined in relation to a
moving perspective. Think of it this way. Imagine that you are driving
a car around the perimeter of the object, marking a line behind you
as you go. From any given point you have eight options. You can continue
to go forward ("F") in the same direction that you have been
going, you can go backward ("B") in the opposite direction,
you can turn to the left ("L") or to the right ("R").
These are the four main points of the compass. The other four directions
are derived from the four basic ones, as can be seen in the compass
to the right. It
is possible to base an eight-directional coding system on relative directions.
Each of the eight directions will be defined in relation to a
moving perspective. Think of it this way. Imagine that you are driving
a car around the perimeter of the object, marking a line behind you
as you go. From any given point you have eight options. You can continue
to go forward ("F") in the same direction that you have been
going, you can go backward ("B") in the opposite direction,
you can turn to the left ("L") or to the right ("R").
These are the four main points of the compass. The other four directions
are derived from the four basic ones, as can be seen in the compass
to the right.
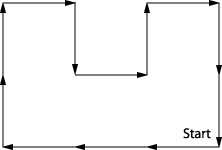
Write down the relative chain code for this figure
on a piece of scratch paper. When you've finished, click the button
that says "See Completed Chain Code" below, and see if you
got it right.
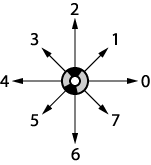
 Just
as we did with absolute chain codes, we can modify the directional
system that we use with relative chain codes, using a numerical system
rather than a letter system. The "forward" direction that
was represented with an "F" is now represented with the
number "2," "Backwards" is "6," "Left"
is "4," "Right" is "0," and so on. Just
as we did with absolute chain codes, we can modify the directional
system that we use with relative chain codes, using a numerical system
rather than a letter system. The "forward" direction that
was represented with an "F" is now represented with the
number "2," "Backwards" is "6," "Left"
is "4," "Right" is "0," and so on.
|
|




 DIRECTIONAL
SYSTEM: Points of a compass
DIRECTIONAL
SYSTEM: Points of a compass
 Since digital computers typically use a numerical system for
storing information (everything is coded in "O's" and "1's")
it will be a step in the right direction to modify our directional system
to a numerical system rather than a letter system. Computer programmers
typically use this system.
Since digital computers typically use a numerical system for
storing information (everything is coded in "O's" and "1's")
it will be a step in the right direction to modify our directional system
to a numerical system rather than a letter system. Computer programmers
typically use this system. It
is possible to base an eight-directional coding system on relative directions.
Each of the eight directions will be defined in relation to a
moving perspective. Think of it this way. Imagine that you are driving
a car around the perimeter of the object, marking a line behind you
as you go. From any given point you have eight options. You can continue
to go forward ("F") in the same direction that you have been
going, you can go backward ("B") in the opposite direction,
you can turn to the left ("L") or to the right ("R").
These are the four main points of the compass. The other four directions
are derived from the four basic ones, as can be seen in the compass
to the right.
It
is possible to base an eight-directional coding system on relative directions.
Each of the eight directions will be defined in relation to a
moving perspective. Think of it this way. Imagine that you are driving
a car around the perimeter of the object, marking a line behind you
as you go. From any given point you have eight options. You can continue
to go forward ("F") in the same direction that you have been
going, you can go backward ("B") in the opposite direction,
you can turn to the left ("L") or to the right ("R").
These are the four main points of the compass. The other four directions
are derived from the four basic ones, as can be seen in the compass
to the right. Just
as we did with absolute chain codes, we can modify the directional
system that we use with relative chain codes, using a numerical system
rather than a letter system. The "forward" direction that
was represented with an "F" is now represented with the
number "2," "Backwards" is "6," "Left"
is "4," "Right" is "0," and so on.
Just
as we did with absolute chain codes, we can modify the directional
system that we use with relative chain codes, using a numerical system
rather than a letter system. The "forward" direction that
was represented with an "F" is now represented with the
number "2," "Backwards" is "6," "Left"
is "4," "Right" is "0," and so on.